Scrap Car Dealers Singapore: Your Essential 2025 Handbook

An Ecosystem of Regulated Disposal
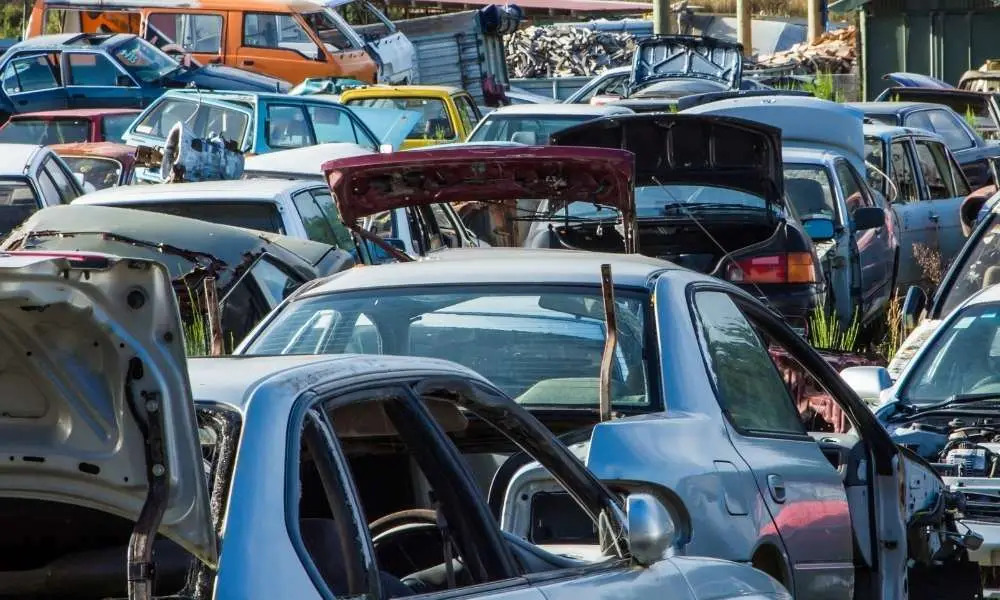
Scrap car dealers Singapore function within a remarkably intricate system, one that exhibits the kind of organizational complexity we might observe in a mature ecosystem where each component serves a specific function and regulatory forces maintain equilibrium. The industry arose from Singapore’s unique approach to automotive management, specifically the Certificate of Entitlement system introduced in 1990 to control vehicle population density on this small island nation. Like adaptive organisms responding to environmental pressures, these dealers evolved to fill a necessary niche: the orderly dismantling and recycling of vehicles that have reached the terminus of their operational lifespan. Understanding this system requires examining its constituent parts, the regulatory framework that governs interactions, and the economic forces that drive behaviour within this carefully bounded marketplace.
The Regulatory Framework as Selective Pressure
In biological systems, environmental conditions determine which organisms thrive and which cannot survive. Similarly, the Land Transport Authority creates selective pressures that shape the industry of vehicle disposal in Singapore. The regulations specify unambiguously that upon deregistration, vehicle owners “must dispose of it by scrapping, exporting, or storing it temporarily in an Export Processing Zone.” This mandate eliminates alternative pathways, channelling all end-of-life vehicles through approved mechanisms.
Scrap car dealers Singapore must satisfy dual licensing requirements, obtaining authorization from both the LTA and holding a General Waste Disposal Facility licence from the National Environment Agency. This dual oversight creates what ecologists might term a filtering mechanism, permitting only operators capable of meeting rigorous environmental and operational standards to participate in the market. The result resembles natural selection: only the most compliant and professionally managed operations persist across time.
Temporal Constraints and Consequences
The system imposes strict temporal boundaries that govern the entire disposal process:
- Eight calendar days maximum for delivering vehicles to LTA-appointed scrapyards after deregistration
- Thirty-day window for submitting disposal documentation to authorities
- Substantial penalties for non-compliance including fines reaching $2,000 or imprisonment up to three months
- Variable processing periods for rebate applications depending on dealer efficiency
These timelines function as regulatory mechanisms preventing vehicles from existing in undefined states between registration and disposal, much as biological systems maintain homeostasis through feedback loops.
The Economic Variables
The financial dimensions of vehicle scrapping involve multiple interconnected factors that dealers in Singapore must integrate when formulating quotations:
Certificate of Entitlement Rebates
The COE rebate calculation represents perhaps the most straightforward component, determined by mathematical formula based on remaining entitlement validity. A vehicle disposed with substantial time remaining recovers proportionally more value than one scrapped near expiration.
Preferential Additional Registration Fee Rebates
PARF rebates apply exclusively to vehicles deregistered before completing ten years of age. This creates a temporal gradient where earlier disposal yields greater financial return, incentivizing proactive rather than reactive disposal decisions.
Physical Asset Valuation
The tangible components of vehicles carry values influenced by materials composition, manufacturability for parts harvesting, and current commodity prices for metals and recyclable materials.
Secondary Market Dynamics
Certain vehicle models support robust markets for replacement parts. Popular manufactures whose vehicles maintain large operational populations create sustained demand for salvaged components, elevating the value proposition for specific models.
Selecting Competent Partners
The diversity among scrap car dealers Singapore requires systematic evaluation to identify optimal partners for this irreversible transaction:
Essential Assessment Criteria:
- Verification of LTA appointment through official governmental databases
- Examination of CaseTrust accreditation indicating compliance with fair trading protocols
- Analysis of customer feedback across multiple platforms revealing consistent behavioural patterns
- Collection of detailed written quotations from minimum three independent dealers
- Direct observation of physical facilities assessing organizational sophistication and environmental compliance
- Request for transparent pricing breakdowns separating vehicle body value from administrative service fees
Observant evaluators note that price variations between dealers can exceed several hundred dollars, particularly for vehicles whose components command premium valuations in secondary markets.
The Deregistration Process
Navigating vehicle deregistration through scrap car dealers Singapore follows established sequential protocols:
- Resolution of all outstanding financial obligations including road tax arrears and traffic violations
- Acquisition of SingPass credentials and T-Pin through advance application
- Selection between self-managed deregistration or authorized dealer representation
- Presentation of original identification documents conforming to regulatory requirements
Environmental Adaptation and Evolution
Singapore’s approach to automotive disposal demonstrates adaptive evolution responding to changing environmental imperatives. The government’s Green Plan establishing 2030 as the deadline for ceasing internal combustion engine vehicle sales represents the latest evolutionary pressure reshaping this industry. Diesel vehicles face even more immediate phase-out by 2025.
Contemporary scrap car dealers Singapore have evolved from simple dismantling operations into sophisticated resource recovery facilities:
- Systematic component extraction maximizing material recovery
- Segregated processing streams optimizing recycling efficiency
- Specialized hazardous materials management preventing environmental contamination
- Closed-loop material flows returning resources to manufacturing supply chains
This evolution mirrors ecological succession, where simple systems develop into increasingly complex, efficient networks of material and energy flow.
Optimizing Transaction Outcomes
Strategic timing and preparation influence final valuations significantly:
- Schedule disposal before COE expiration maximizing rebate recovery
- Remove personal belongings systematically from all vehicle compartments
- Maintain reasonable vehicle presentation despite end-of-life status
- Compare multiple quotations accounting for comprehensive service scope
- Evaluate dealer processing efficiency recognizing that payment delays carry opportunity costs
Synthesis and Conclusion
The landscape of vehicle disposal in Singapore exemplifies how regulatory frameworks, economic incentives, and environmental considerations combine to create functional systems serving public policy objectives. Like natural ecosystems achieving stability through balanced interactions among diverse species, this industry maintains equilibrium through careful regulation, competitive market forces, and evolving environmental standards. Success within this system requires understanding its fundamental mechanisms, preparing thoroughly for the transaction process, and selecting partners whose operational sophistication matches the complexity of the regulatory environment. When vehicle ownership reaches its natural conclusion, informed decision-making based on systematic evaluation yields optimal outcomes when engaging Scrap car dealers Singapore.